The covid world has given opportunity to have a closer look at the fundamentals of disease.
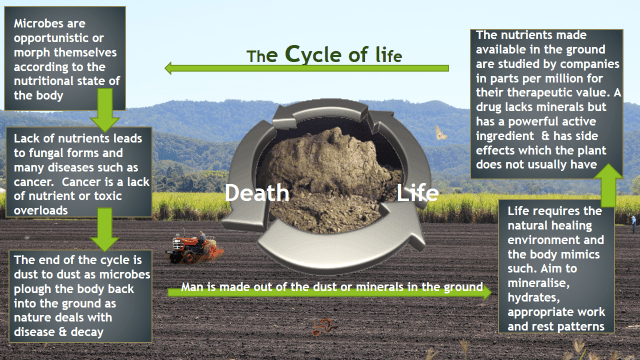
The body machinery works off laws. You say what laws? Such laws are evident in physics, flight, electricity etc. The laws spoken of here such as rest patterns, removing free oils, inhaling fresh air in ventilated rooms etc. The result is to be ideally an internally clean, nutrient-rich system for self-healing.
Years ago I was told that some scientists believe that viruses are actually fungal spores. It did not make sense that a nonliving entity was responsible for disease- there was something wrong with the foundational premise for disease because of partial truths. A virus is not a microbe for it is not alive until it is deposited into the living host and the word virus by association to disease is actually a very poor term. Only recently has it been understood that a virus is necessary for the creation of life in the initial cell replication for the formation of the fetus and continues to disperse throughout the cells as replication continues.
Extracellular vessels, EVs are important in cell-to-cell communication as well as pathogen-to-pathogen communication. EVs are small phospholipid membrane-enclosed entities that can carry microRNA (miRNA). A miRNA is a small single-stranded non-coding RNA molecule (containing about 22 nucleotides) that functions in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. As scientists study deeper into this subject the line blurs between a virus and an EV and are now being exploited for vaccine technology. An example of fungal EVs contain RNA, proteins, melanin, lipid, and polysaccharides. EVs are fundamental to the complex cycle of life. EVs of bacteria can protect against disease supporting commensal growth or be pathogenic promoting inflammation in the host. EVs become indistinguishable from viruses the deeper we search. EVs associated with extracellular activity in the body could be broadly known as membrane vesicles, are found in great abundance in the water we drink and the air we breathe and of course the earth we take our food from. Microbes are affected by environmental factors through membrane vesicles. The microbes or cells are transformed accordingly. Viral payloads make life and its function possible and microbes make up the gut function without which we would not have immunity, get our nutrition or be able to function at all. Microbes morph themselves according to the environment in which they are found by EVs or membrane vesicles. This determines blood flow and quality and our self-healing.
There is vertical replication of the cells but also the horizontal influences by environmental factors and the outcome depends both on internal as well as external hygiene. This makes up the cycle of life allowing recycling and the regeneration of organic matter. ‘Extracellular vessels important in cell to cell communication or EVs, depending on the proteins and genetic material incorporated in them, play a significant role in viral infection, both facilitating and suppressing it.’
‘EVs can bind to the plasma membranes of other cells, enter them either through fusion or endocytosis, and trigger specific reactions from these recipient cells. Finally, EVs carry genetic material, and this genetic material can change functions of the recipient cell.’ Extracellular vesicles and viruses: Are they close relatives? Esther Nolte-‘t Hoen, Tom Cremer, Robert C. Gallo, and Leonid B. Margolis
If we were to let the body become filthy inside, the gene expression through EVs would mean life-threatening parasites, bacteria and fungus would rapidly multiply and if present in a group could cause an epidemic that would cause death and plow us back into the ground thus recycling life and cleaning up the filth.
The body has several lines of defense against attack. When the last body defense has been broken in which the person is infected by disease this becomes part of the DNA thus a weak chain remains in the system rather than strengthening immunity. When the immune system is compromised the disease returns but has changed form and location, chickenpox presents as singles for example. Thus whatever enters the system can permanently remain thus potentially weakening the system and causing further disease or one disease leading to another. This is contrary to the concept of compromising the system for an immune response that may have immediate but not long-term benefits.